PFNA belongs to a new type of proximal femoral internal fixation system, which is a newly improved PFN (proximal femoral intramedullary nail) system. On the one hand, it inherits the advantages of the original PFN with the same biomechanical characteristics, and on the other hand, it has innovative specific design, making fixation more effective and operation simpler.
Surgical Procedures and Techniques
Instruments: fracture kit, bending disc, electric drill (with strong power); Manufacturer PFNA internal fixation device (Weiman or Kanghui), electric knife
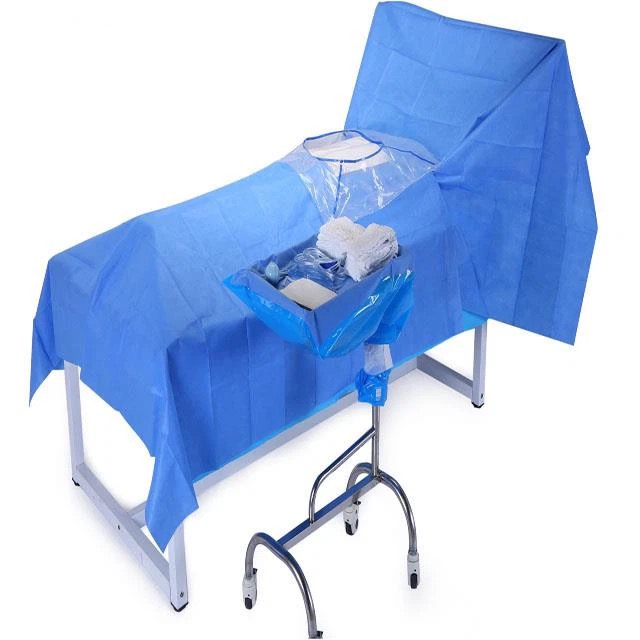
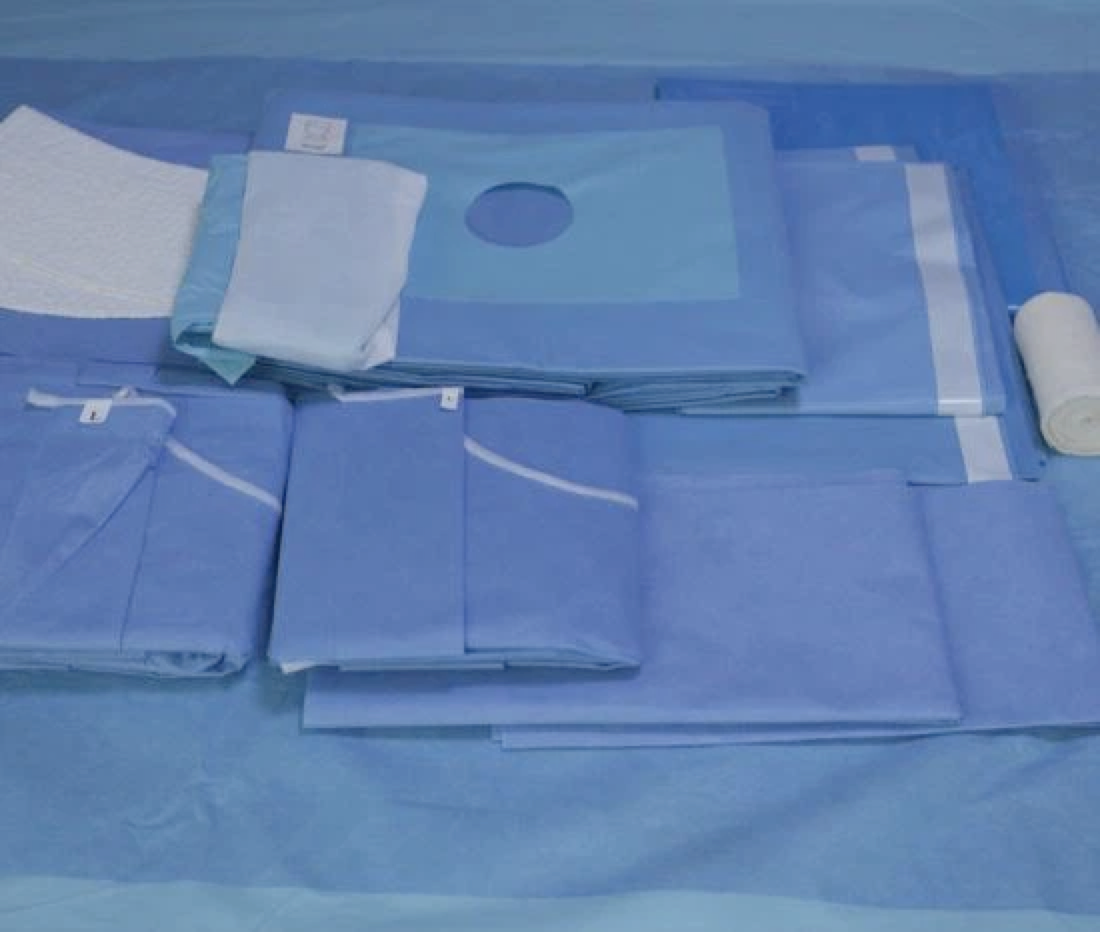
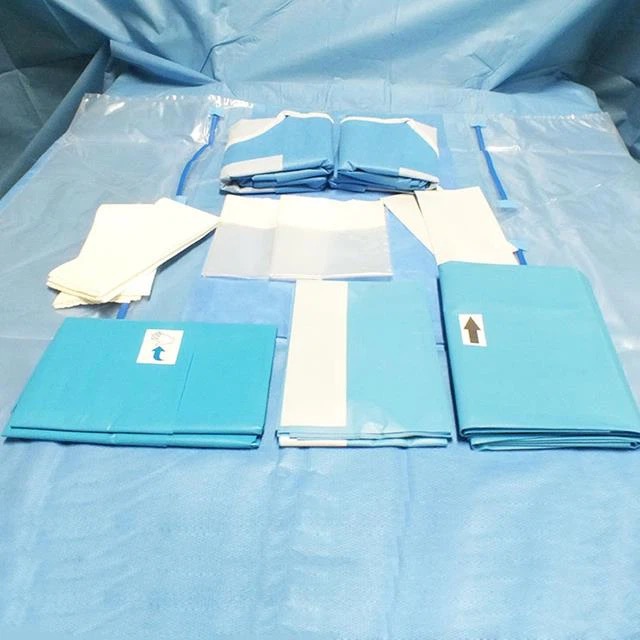
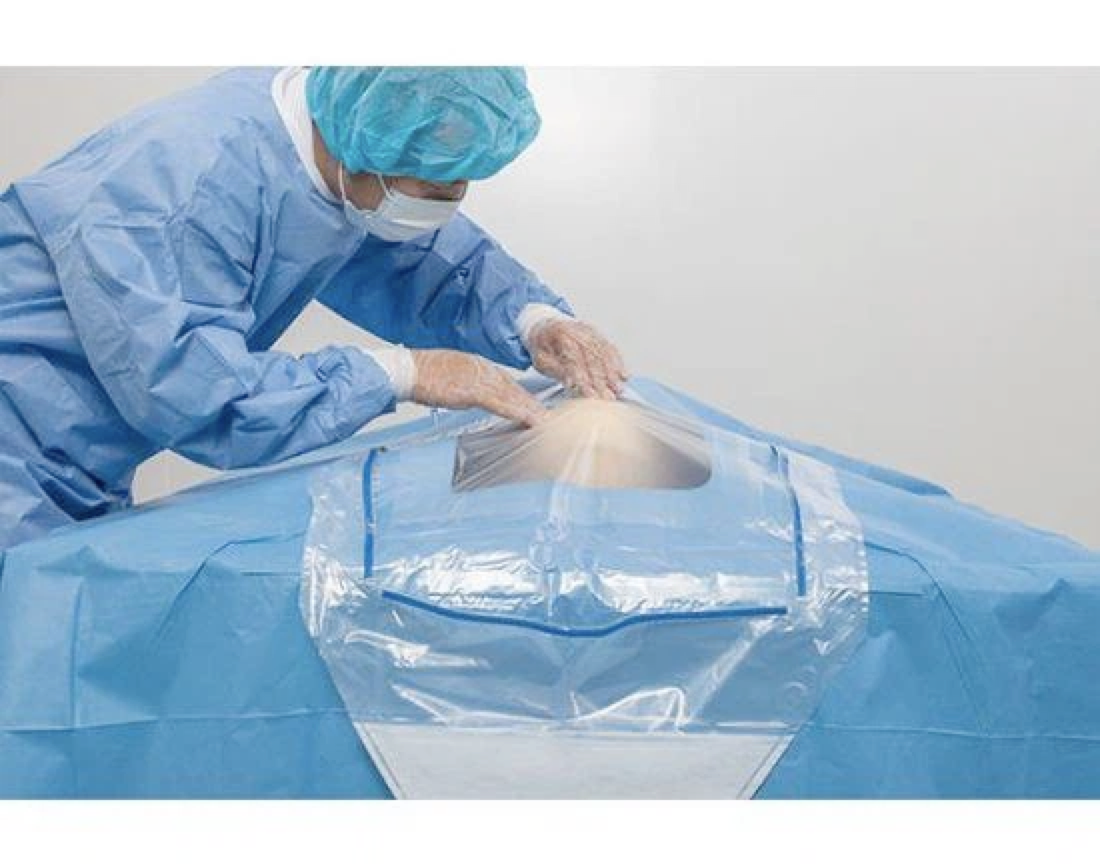
Dressing: laparotomy bag, surgical gown, joint dressing, holding bucket, disposable waterproof hole towel.
Disposable items: cotton pad, elastic bandage, bandage, 50 * 60 adhesive towel, 45 * 30 adhesive towel, 2/0 mousse thread, 2/0 absorbable thread, 1/0 absorbable thread, 9 * 34 sewing needle, suction tube, suction head, physiological saline, gloves, blade size 23, nail device, fluoroscopy sheet, X-ray machine cover.
Instruments and equipment: high-frequency electric knife, power system, traction bed, X-ray machineposition
Lie on your back on the traction bed, with the affected side pressed against the bedside, your hips level with the lower edge of the bed, and a barrier pillar placed in the perineum.
Place the affected lower limb with an abduction of 30 ° and an internal rotation of 15 ° on the foot traction frame, while the hip and knee joints on the healthy side are excessively flexed. Place a bracket behind the middle and upper segments of the calf and fix it, paying attention to protecting the popliteal fossa from compression.
The affected upper limb is fixed in the elbow flexion position in front of the chest to prevent obstruction of the surgical operation, while the healthy arm is extended onto the support arm frame.
Secure the patient to the operating table with a strap on the chest to prevent falling.
After the positioning is completed, tighten the nuts of each joint of the traction frame once again to prevent intraoperative loosening and pose complications that may affect the smooth progress of the surgery.