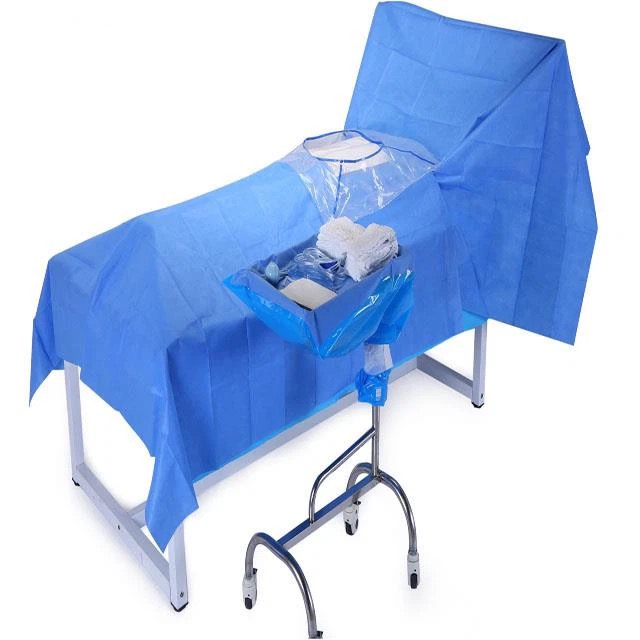
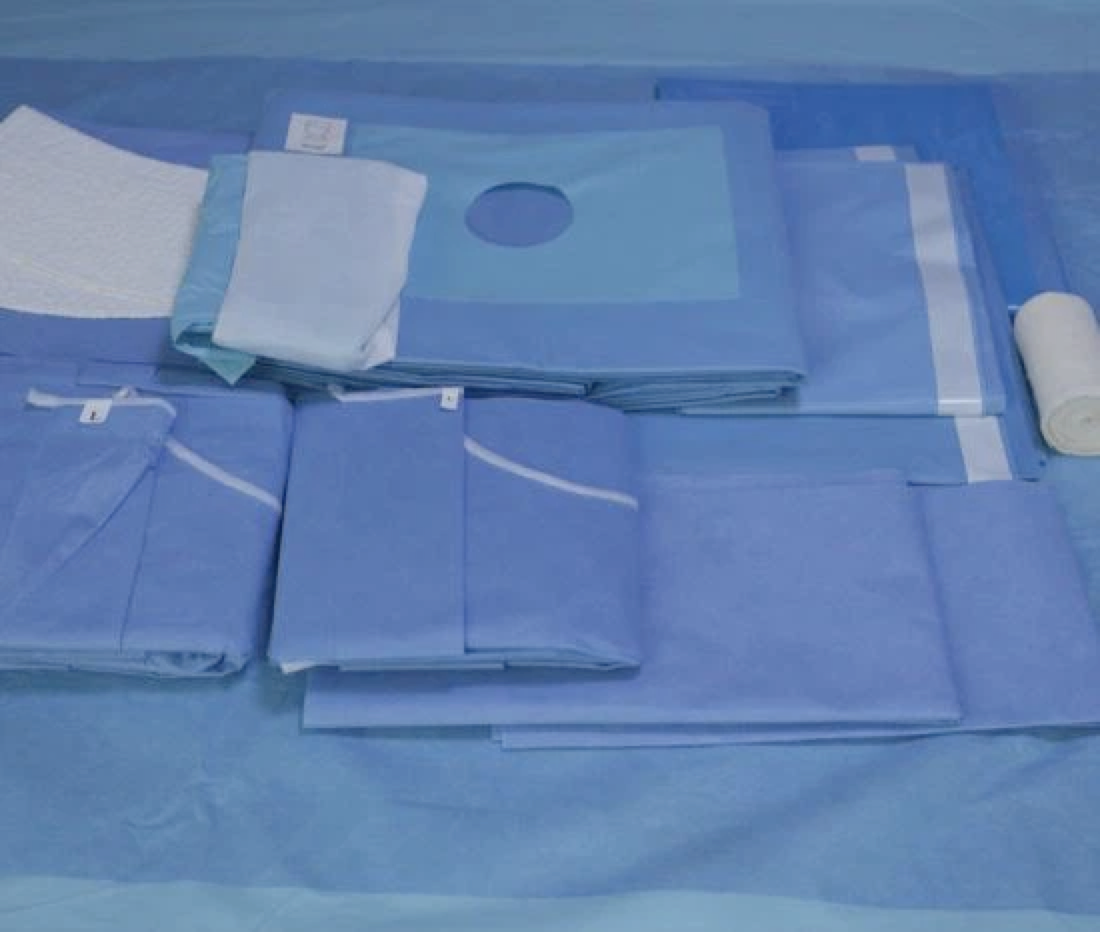
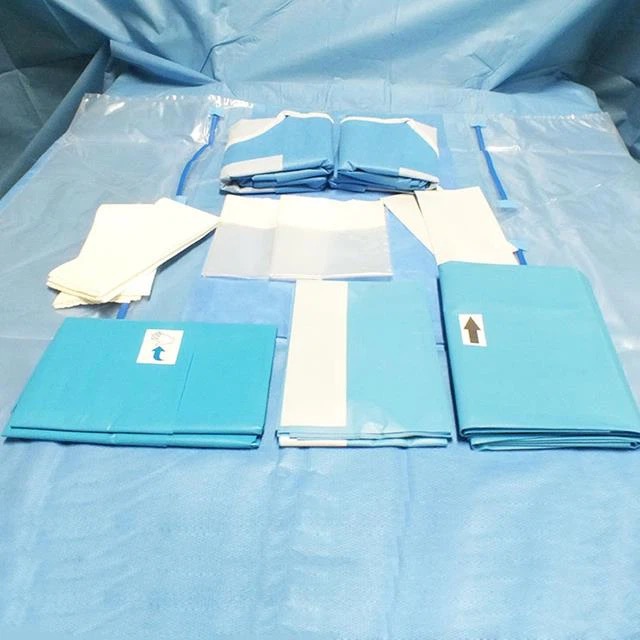
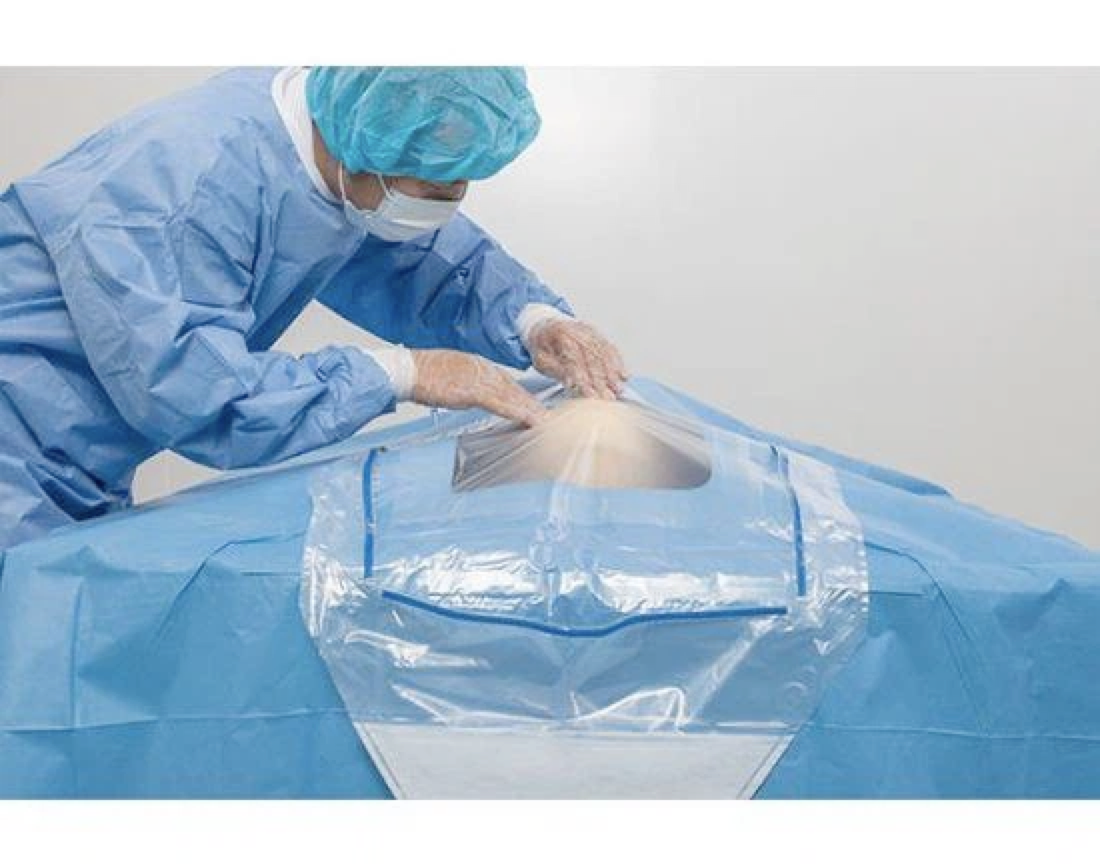
01.Preparation for beach chair position placement
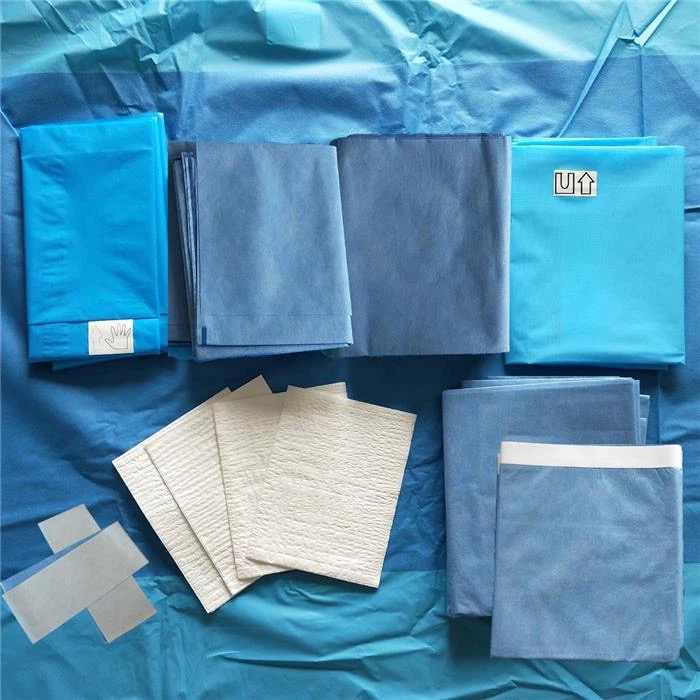
For beach chair position placement, we need to use cotton cushion covers, rectangular pillows, positional braces, hand rests, and restraining straps. In addition, a shoulder arthroscopy brace can be selected according to the configuration of the hospital. The brace can remove the back plate to facilitate intraoperative shoulder joint movement and fluoroscopy, and the head is fixed and can be adjusted according to the patient's body shape.
02. Positioning of the beach chair
Remove the foot plate of the stent and keep the head plate. After the patient is anesthetized, work with the anesthesiologist and the attending surgeon to complete the position of the beach chair. Under the premise of ensuring a good surgical field of vision, the patient will be fixed firmly. First, the patient is placed in the head-down-foot-high position, and then the patient is elevated as a whole, and a stopper is placed on the healthy side of the hip to prevent the patient from falling out of bed when the surgical bed is tilted to the healthy side. The handrail is placed in an appropriate position so that the patient's arm is in a functional position. According to the actual need, the surgical bed can be tilted to the healthy side to fully reveal the shoulder.
03. Toweling sequence for beach chair position
It is recommended to use disposable therapeutic towel to spread the towel in order to achieve the purpose of waterproof. The order of application of the towels is as follows:
The axillary toweling is performed first, covering as much of the patient's axillary hair as possible.
Then proceed to the head to lay the towel, it is recommended to lay the towel from the center to the sides, so as to facilitate the operation.
The tablecloth covers the body and tray;
Enhance head coverage with a larger therapeutic towel on top of the head toweling;
Use a U-shaped single encircling incision, taking care to tape it securely without leaving a gap to avoid intraoperative fluid leakage;
Wrapping the hand with a cuff, wrapping it tightly with a bandage from proximal to distal and fixing it to the patient's skin with tape to prevent the cuff from falling off and fluid leakage;
Finally, the cavity towel is laid, taking care to expose the patient's shoulder and secured with tape.
04、Application of shoulder arthroscope in beach chair position
1. Positioning points: When positioning, the patient should take a 60°-70° semi-sitting position, with the knee flexed and tilted to the healthy side by 20°-30°, in order to obtain full exposure and facilitate intraoperative operation.
2、The advantages of beach chair position:
①The upper arm can be moved freely during the operation to move the shoulder joint and increase the exposure;
②Simple to set up and less time-consuming;
③Can check the contralateral shoulder joint, especially suitable for patients who need to perform bilateral shoulder surgery;
④ For patients who cannot be handled microscopically, it is easy to intermediate to open surgery;
⑤ Suitable for general anesthesia or brachial plexus anesthesia;
⑥No need for traction, no damage to the brachial plexus nerve;
⑦ Better patient comfort and reduced risk of pressure injury.
3. Disadvantages of beach chair position:
① Difficult to operate behind the scapula;
② Intraoperative traction is not possible, and good exposure cannot be obtained by increasing the joint space;
③ Prolonged surgery in the sitting position can lead to decreased cerebral blood flow;
④ Lens water ingress and fogging.
Treatment:
① Elevate the upper body by 60°-70° to favor the operation of the posterior scapula;
② Due to the presence of a certain tilt of the acromion, the surgical bed can be tilted 20°-30° toward the healthy side to increase the exposure;
③ Continuous pumping of water in the joint cavity can avoid fogging of the lens;
(iv) Intraoperative cerebral oxygen monitoring and catheterization to observe access.
05、Beach chair position of shoulder joint replacement application
Shoulder replacement can be performed in modified beach chair position, in which the patient's upper body is elevated by about 40°-50°, the patient adopts a semi-sitting position, suspends the shoulder of the affected side, and the knee joint is flexed, with a soft pillow under the knee.
06, beach chair position of the proximal humerus fracture application
Proximal humerus fracture surgery can also adopt the modified beach chair position, elevate the patient's upper body by 40°-50°, semi-sitting position, make the knee flexion, and put a small square pillow behind the affected scapula, elevate the suspension of the affected shoulder by about 10cm, and put a soft pillow under the knee.
07, beach chair position of clavicle fracture application
The patient's upper body is elevated by 40°-50°, semi-sitting position, knee flexion, a small square pillow is placed behind the scapula on the affected side, the affected side's clavicle is elevated, the head is tilted to the opposite side, and a soft pillow is placed under the knee.
08, beach chair position placement of attention and intraoperative pressure injury prevention
1. Secure the joints of the positional support;
2. Avoiding the patient's hair by sticking the adhesive tape, avoiding the compression of the auricle and facial nerve;
3. Avoid pressure at the bony prominence;
4, Intraoperative drip try to choose the lower limbs for puncture;
5. Pay attention to the protection of eyes and maxillofacial skin;
6.Emphasis on cooperation with anesthesiologists to ensure that all kinds of tubes are in place, and actively prevent the emergence of hypoperfusion of brain tissue and hypothermia in patients during the operation.
09. Management of intraoperative hypothermia in the beach chair position
1. Effects of intraoperative hypothermia on the body
Circulatory system: it is easy to cause ventricular extrasystole of the heart, slow pulse and lowered blood pressure, resulting in slower blood flow to internal organs, slow metabolism of the liver, and increased accumulation of drug toxicity.
Respiratory system: hypothermia increases carbon dioxide solubility in the hematoma and decreases blood pH, easily leading to acidosis.
Circulatory system: hypothermia makes blood viscosity increase, which slows down blood flow, prolongs coagulation time, and increases surgical bleeding.
Surgical incision healing: Hypothermia decreases white blood cells, thereby decreasing the body's own physiology and immunity, increasing the chance of incision infection and lung infection.
2. Factors causing hypothermia during surgery
There are many factors that can cause hypothermia during surgery, mainly including the environmental factors in the operating room, surgical disinfection and incision exposure, the use of a large amount of irrigation fluid, anesthesia factors, intraoperative fluid intake factors, and the patient's own factors.
3. Prevention and treatment of hypothermia
Intraoperative application of a warmer to maintain the patient's body temperature;
Intraoperative continuous temperature monitoring;
Intraoperative use of a fluid warmer, especially for patients who need to use a large amount of fluid during surgery.