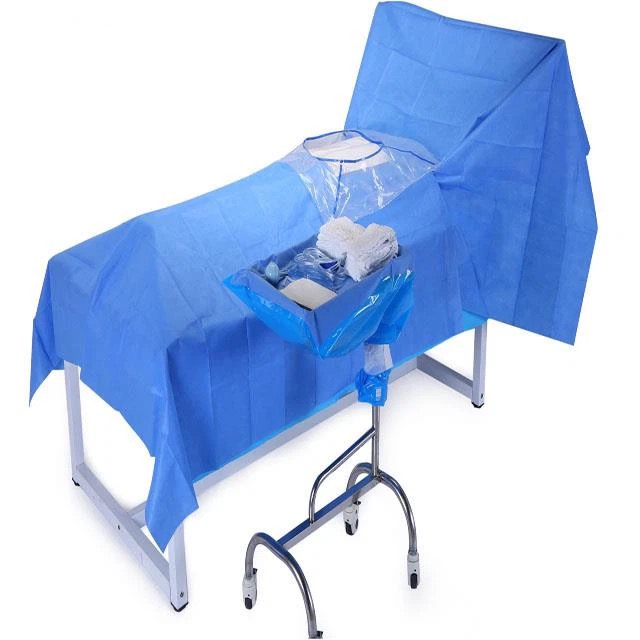
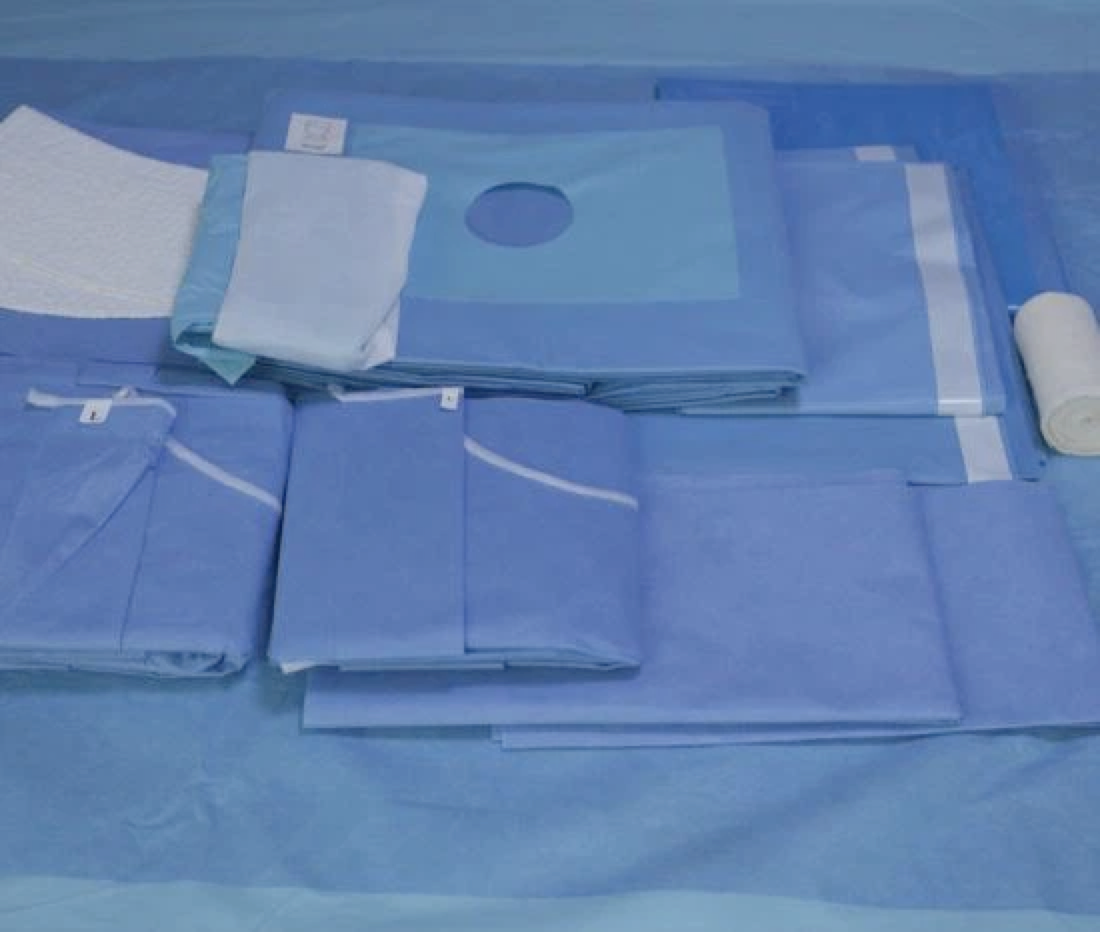
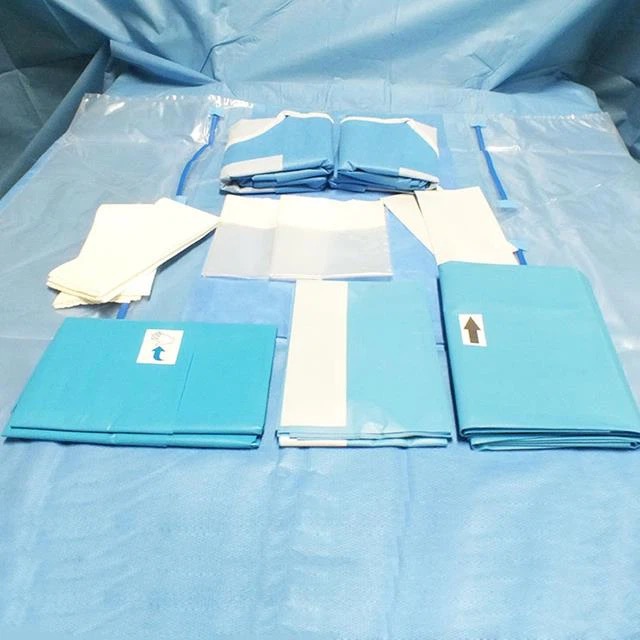
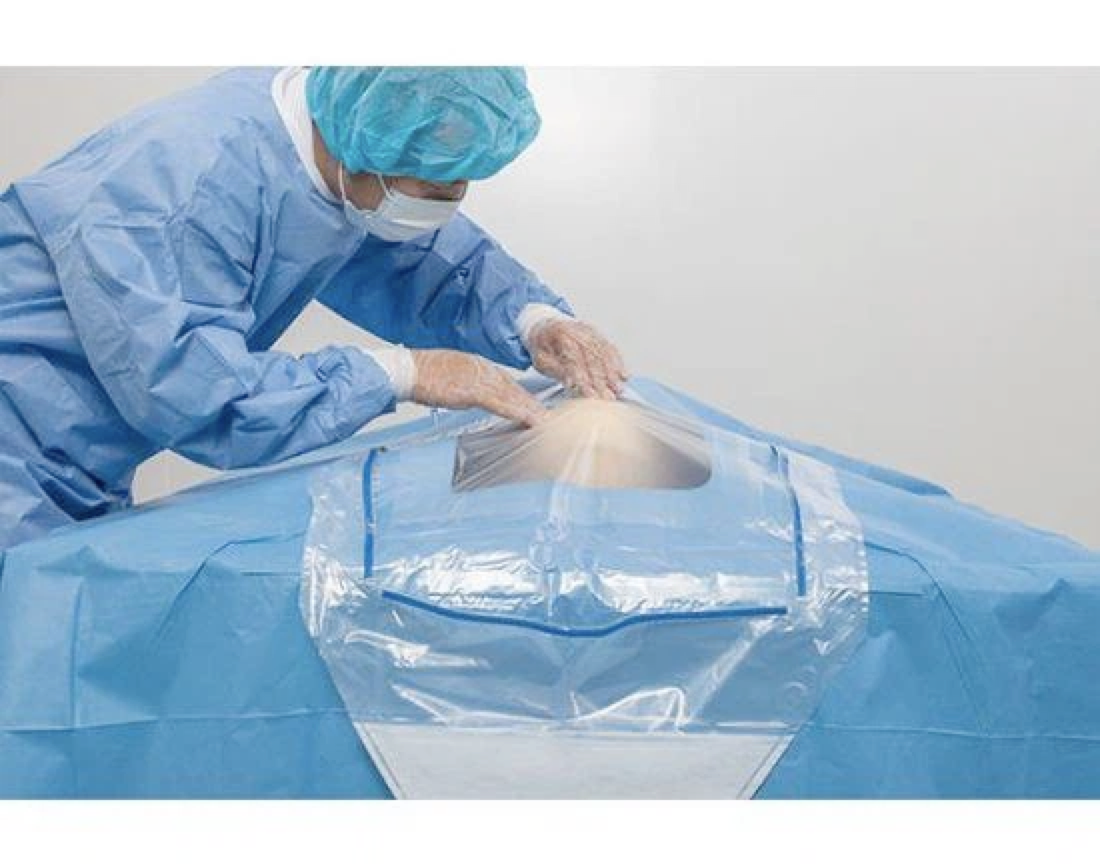
Blood bags after transfusion usually need to be kept for 24 hours because transfusion reactions usually occur within 24 hours, and no adverse transfusion reactions after 24 hours after the transfusion can be kept without further storage.
The process of taking blood from one person and feeding it into another is called transfusion and is commonly used clinically for conditions such as bleeding conditions due to surgery, severe trauma, anemia or low protein disorders, serious infections and clotting abnormalities. In order for the transfusion to be successful, the lectin on the surface of the donor's red blood cells must correspond to the recipient's lectin, i.e., the blood types of the donor and recipient must be compatible, otherwise the antibodies (lectins) within the recipient's blood will attack the donor's blood cells and form a blood clot through an agglutination reaction.
Therefore, patients need to pay attention to blood type matching during blood transfusion, i.e. the ABO blood type of the donor and recipient is the same, to ensure that no hemolytic reaction will occur. At the same time, adverse reactions such as fever and allergy may occur after blood transfusion, at which time the family should promptly explain the situation to the medical staff and take appropriate treatment measures.