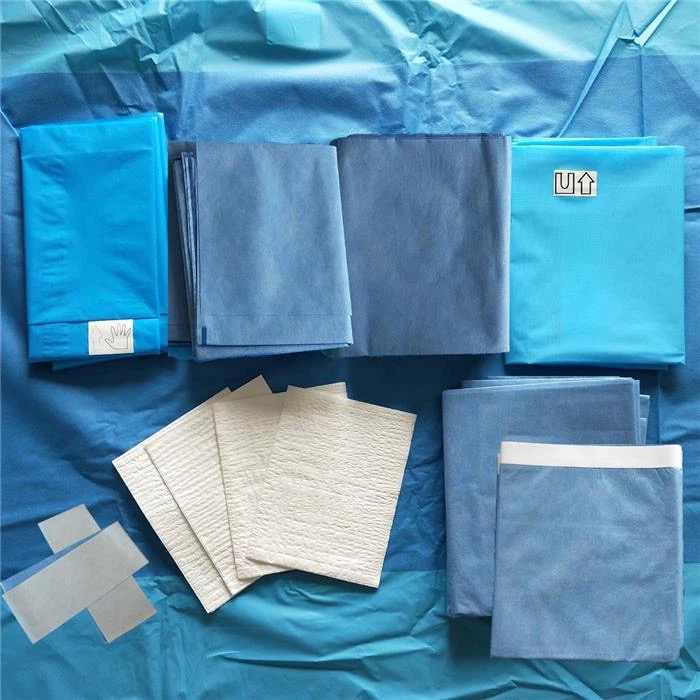
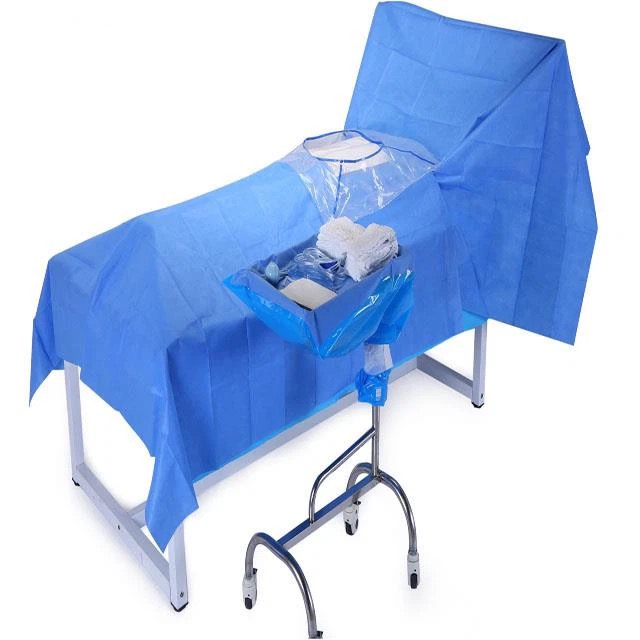
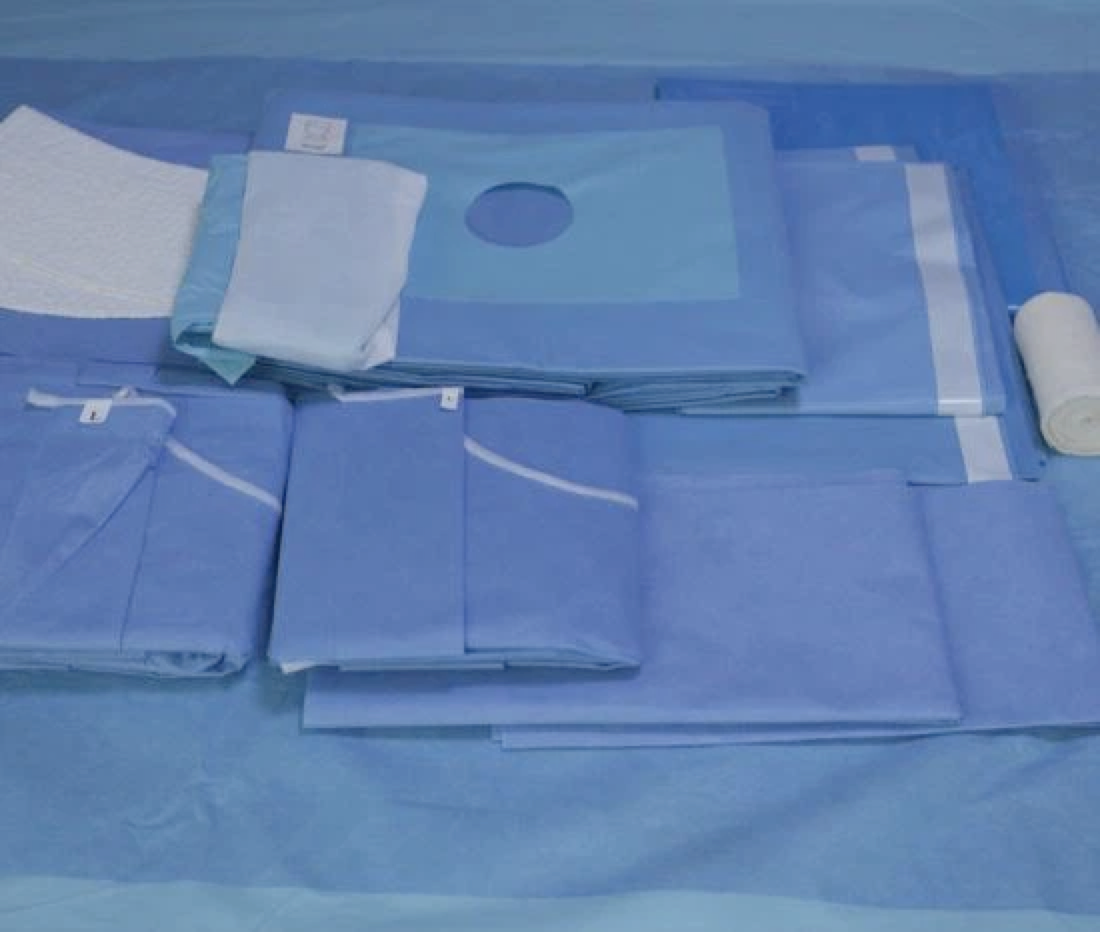
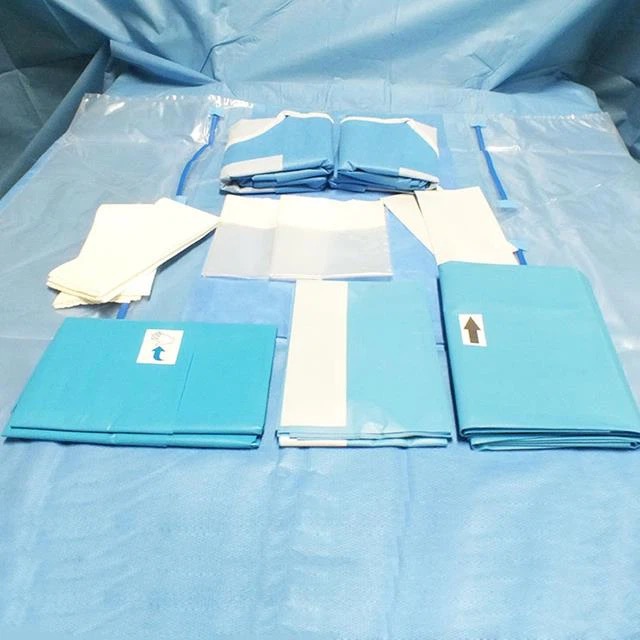
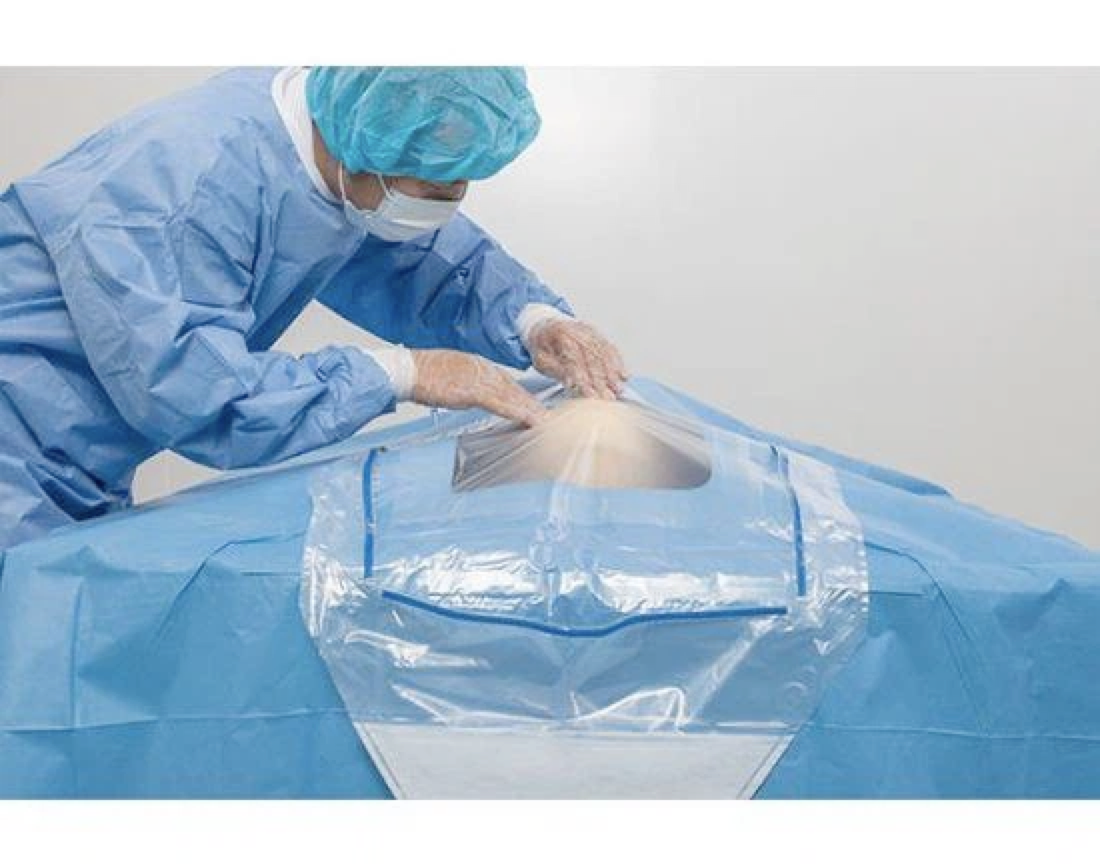
Surgical gowns are used by personnel in medical operating rooms or decontamination laboratories. For use during surgery where the patient's blood is free of infectious viruses. It is used to be worn on surgeons and nurses to prevent the spread of dander from the surgeon's body to the open surgical wound wound and to prevent the spread of body fluids from the surgical patient to the medical staff, providing bi-directional biological protection.
Isolation gowns are used to protect medical personnel from blood, body fluids and other infectious materials, or to protect patients from infection. They are commonly used in operations where splashing of blood and body fluids may occur; when in contact with patients with infectious diseases and multi-drug resistant bacteria transmitted by contact; and when performing protective isolation on patients with extensive burns and bone marrow transplants.
Surgical gowns made of nonwovens provide a reliable protective barrier with good impermeable barrier function and bacterial resistance to liquids. From the comparison of protective ability, surgical gowns are superior to isolation gowns, so surgical gowns can be used instead of isolation gowns.
Since isolation gowns cannot be discarded once they are put on during use and need to be put on and taken off in strict accordance with regulations, the operation is tedious and easily contaminated, so they need to be cleaned and disinfected after use. Surgical gowns are easy to take on and off, so some hospitals use surgical gowns instead of isolation gowns.