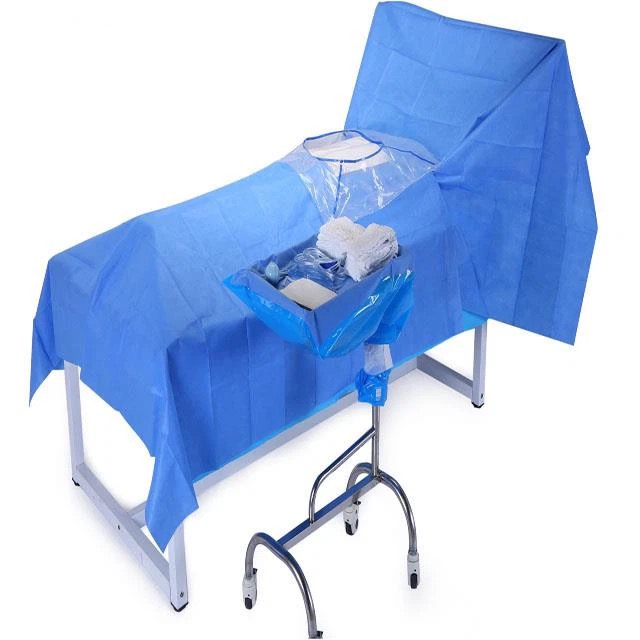
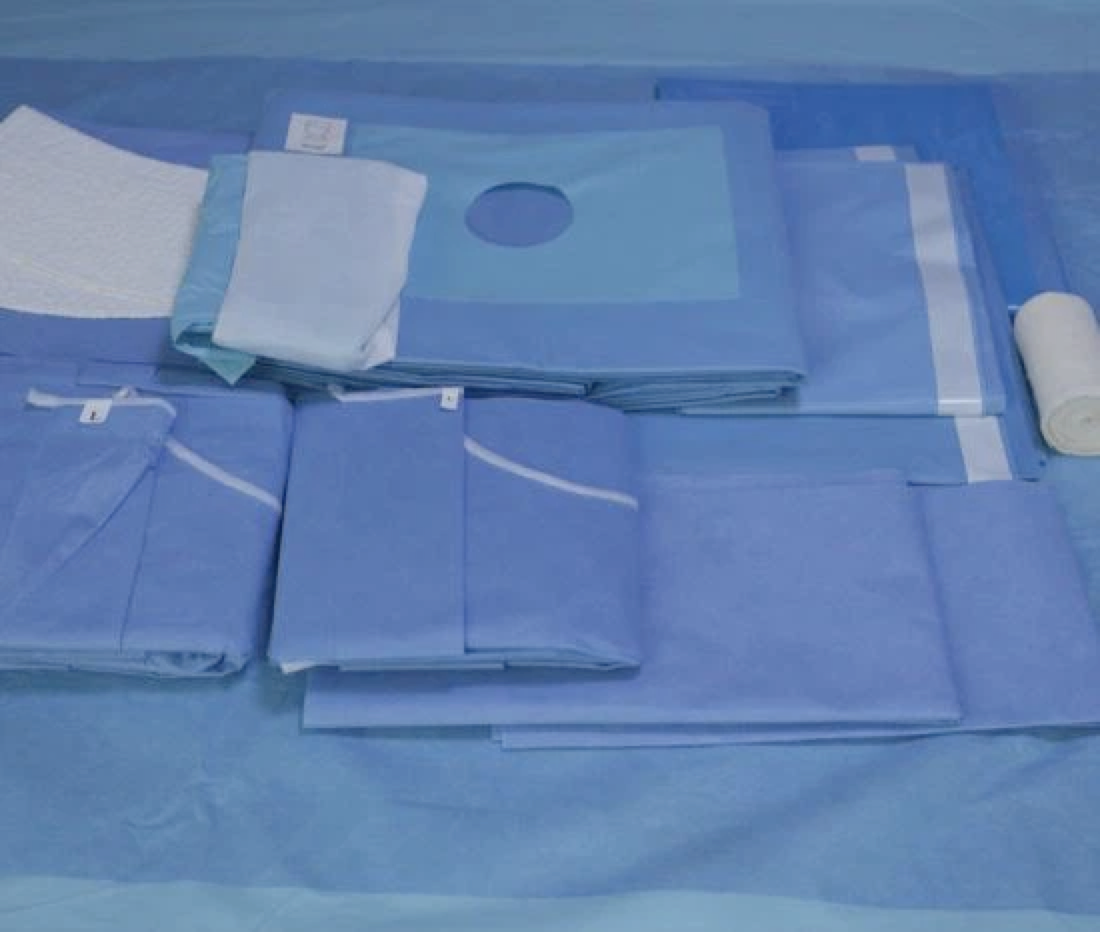
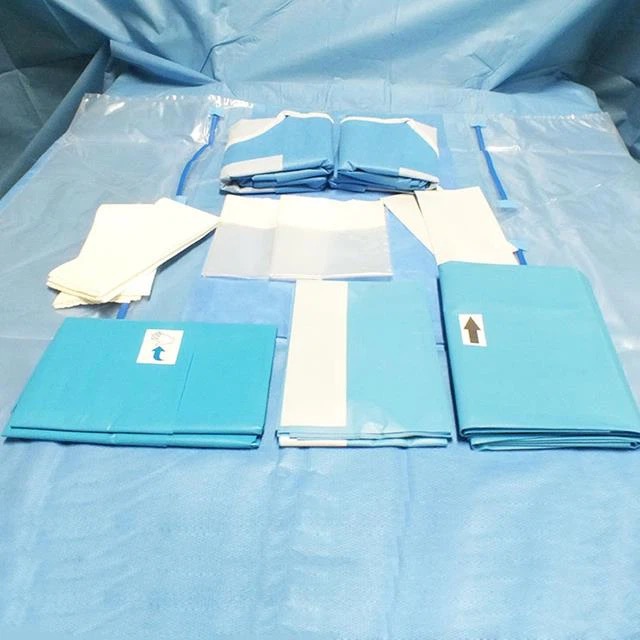
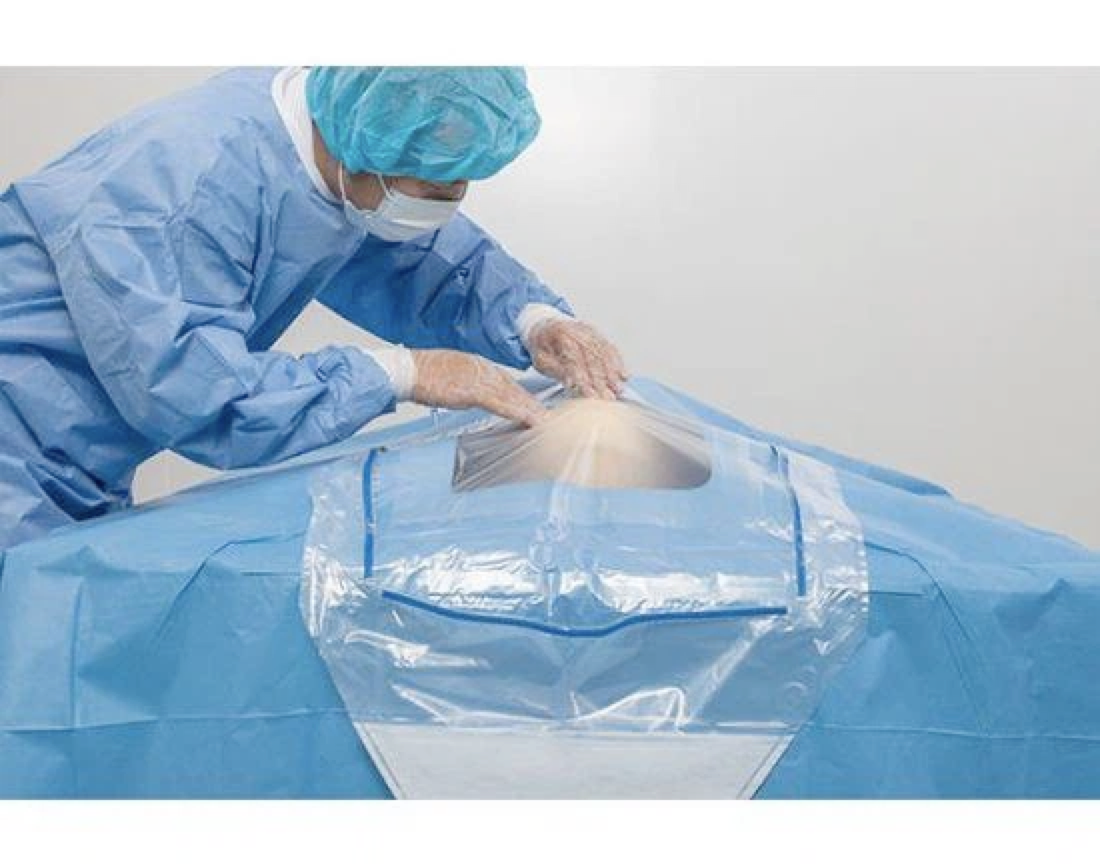
01. Curved vascular forceps: also known as hemostatic forceps, used for separating and clamping tissues or blood vessels to stop bleeding, and to assist in suturing.
02. Straight vascular forceps: also known as hemostatic forceps, used for subcutaneous tissue hemostasis.
03. Right angle forceps: used to free blood vessels, nerves, ureters, biliary tract and other tissues and guide traction.
04. Tissue scissors: referred to as curved scissors, there are long, short, sharp and blunt. Used for freeing and cutting superficial and deep tissues.
05. Wire scissors: short for straight scissors, used for cutting wires and dressings.
06.Scalpel: made up of knife handle and blade, there are various models of knife handle and blade, used for cutting and dissecting different tissues.
07.Surgical Forceps: The tips of forceps are divided into two categories: toothed and non-toothed, with length and thickness for holding, assisting dissection and suturing tissues.
08. Needle holders: different lengths and straight and curved, used for holding suture needles and assisting in knotting sutures.
09. Suture Needle: It consists of three parts: the needle tip, the needle body and the needle eye. The tip of the needle is divided into round and triangular needles; the body of the needle has different curvatures, divided into straight needles, 1/2 arc, 3/8 arc 3 arcs. Used for sewing various tissues.
10. Towel clamp: used to fix the dressing and protect the incision.
11. Caustic forceps: also known as toothed straight forceps, used for clamping thicker tissues and tissues that are easy to slip off, can also be used for the removal of tissue clamping traction. The hooked teeth at the anterior end can prevent slippage, and the damage to the tissue is large, and cannot be used for general hemostasis.
12. Tissue forceps: also known as rat-toothed forceps, Alice forceps, used to clamp the gauze pads and incision edges of the subcutaneous tissue, but also used to clamp the tissue or flap as traction.
Picture
13. Appendiceal forceps: used for lifting and fixing the appendix or ureter and other tissues.
Pictures
14. Lung lobe forceps: used for lifting and tractioning the lung lobes to visualize the surgical field.
Pictures
15. Gastric forceps: used to clamp the stomach or colon stump. The shaft is multi-jointed, with high force and strong compression, and the tissue is not easily dislodged.
Pictures
16. Intestinal forceps: There are two types of forceps, straight and curved, used for clamping the intestinal tube, with thin and fine teeth grooves, and small pressure effect on the tissues.
Picture
17. Suction head: with different lengths, curvatures and calibers. It is used for suctioning out blood, body fluids and irrigation fluids from the surgical field to maintain a clear surgical field.
Pictures
18. Bone scissors: used for trimming bone tissue.
19. Bone biting forceps: used for biting off and trimming bone tissue.
20. Periosteal stripper: for stripping the periosteum.
21. Nerve Stripper: for stripping and separating nerve roots.
22. Bone file: Used to file the broken end of the bone and make it blunt to avoid piercing the tissue and causing bleeding.
23. Bone chisel: used for removing bone scabs and cutting off bone pieces, divided into flat chisel and round chisel.
24. Bone hammer: Used to assist the bone chisel to cut the bone and implant or remove the object.